Have you ever spent hours perfecting a vibrant, digital design, only to have it print looking dull, muddy, and completely unlike what you saw on your screen? This frustrating colour disconnect is one of the most common pitfalls in design, and it often stems from a fundamental misunderstanding of how colour works in print versus digital. The solution to achieving true-to-life, professional results lies in mastering the essential language of print colour: the CMYK colour model. This isn’t just technical jargon; it’s the scientific backbone of every magazine, brochure, and custom packaging box you’ve ever admired. Understanding CMYK is the non-negotiable first step to ensuring your brand’s colours are consistently reproduced with pinpoint accuracy. At Packaging Bird, we don’t just use this model; we master it to guarantee your packaging always makes a stunning and flawless first impression. Ready to demystify the process and ensure your designs always translate perfectly from screen to physical product? Let’s dive in.
What is the CMYK Colour Model?
The CMYK is an abbreviation for C is for Cyan, M is for Magenta, Y is for Yellow, and K is for Key (Black). These are the four main inks that are used for printing processes, and this produces a full spectrum. Other than that, unlike RG, B, which is based on light, CMYK is based on ink pigments. By layering these pigments and colours, you can create different types of colours and designs. These are the same kind of colours and pigments you see in magazines, books, and other stuff. So, now we know that the CMYK model is so important.
Read More: What is CMYK in Custom Printing?
CMYK Vs RGB
One of the most common questions is what the difference is between CMYK and RGB. Well, the answer to this question is quite simple. RGB is basically red, green, and blue. This is used for different digital devices like monitors, TVs, and smartphones. This means that it is an additive colour mode, and by mixing them, you can get different colours. CMYK, which is cyan, magenta, yellow, and black. This is used for printing. It is a subtractive colour model, meaning colours are formed by subtracting light, as inks are simply layered on the paper. So, just to clear the confusion, if you are going for screen use RGB, and if you are someone who wants to go for printing, then go for CMYK. If you use it otherwise, it can be very dull.
How the Colour Wheel Works
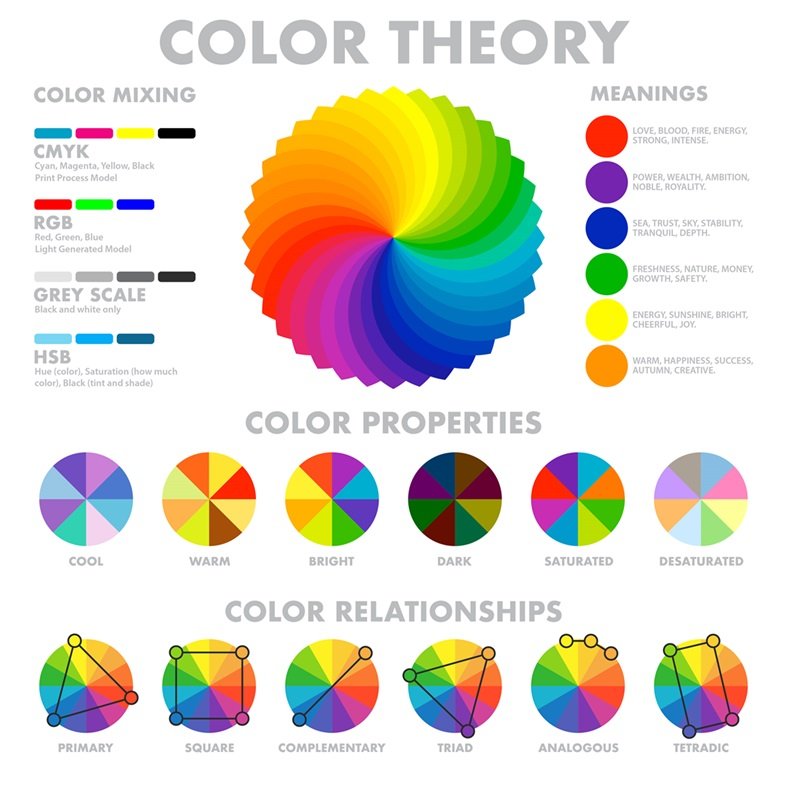
The CMYK colour wheel is built on subtractive colour mixing. RGB pigments are quite different; however, CMYK pigments are quite different.
- Cyan and Magenta Blue tones
- Magenta and Yellow Red Tones
- Yellow and Cyan Green Tones
- Cyan + Magenta + Yellow = dark brown/black tones
CMYK alone cannot really produce any type of true black; printers themselves add the black color to it. They can make the sharpness, richness, and clarity.
CMYK in the Printing Process
The printing process really relies on the CMYK printing, which is also known as the four-color printing process. And this is how it works;
1. Separation
The design is separated into the first step. This is separated into four colours, which are cyan, magenta, yellow, and black.
2. Dot Patterns
Each colour is then printed into different types of dots. The human eye has the tendency to simply blend these colours and make them into smooth images.
3. Layering
The third step is to overlap different types of dot percentages and printers create different illusions of full-colour images.
4. Final Output
The result is a full and vibrant colour. These are the four steps that are needed for all the printed designs.
Tools For CMYK Colors
Designers and printers rely on different specialized tools;
- CMYK Colour Chart: This means the variety of colours that are made with different ink combinations.
- CMYK color palette: These are the predefined sets of harmonious colors that are used for branding
- CMYK colour picker: These are the ones that can be used, made by different software. Some of the most popular types of software include Photoshop, Illustrator, and InDesign.
- CMYK colour generator: Converts RGB hex codes into different colour codes.
These are the kinds of colour codes that you need for the creation of different designs.
What are the Benefits Of CMYK Colour Model?
Understanding the benefits of the CMYK colour model is crucial for any successful print project. This subtractive color process is the industry standard for a reason: it delivers exceptional colour accuracy and consistency across a massive range of materials, from vibrant marketing brochures to premium custom packaging. By utilizing Cyan, Magenta, Yellow, and Key (Black), the CMYK system allows for a vast spectrum of rich, deep colors and precise tonal variations through halftoning. This translates to cost-effective, high-quality mass production without sacrificing brand integrity. For businesses, this means reliable and predictable results every time, ensuring your brand’s colors are perfectly reproduced on every physical product you create.
Limitations For CMYK Printing
There are some kind of limitations for CMYK printing. These are some limitations that you should keep in mind;
- Color Range: CMYK cannot really produce the same type of colors or spots that RGB can produce.
- Vibrancy Loss: Bright and neon kinds of shades are very hard to achieve.
- Screen to print mismatch: designs that are created in RGB may look very different when they are converted to CMYK.
This is the sole reason why designers and painters really prefer to use Pantone spot colors alongside CMYK for special types of branding projects.
Applications Of CMYK In Different Industries
There is a reason why the CMYK model really dominates different industries. Here are some of the applications of CMYK;
- Marketing Collateral: flyers, brochures, and posters
- Packaging: labels, cartons, and different wraps
- Publications: for magazines, newspapers, and books
- Branding materials: business cards, stationary, and catalogs
- Large format prints: banners, signage, and billboards
Final Thoughts
In the world of physical design and print, the CMYK colour model is not merely an option—it is the essential foundation. Mastering its subtractive principles is what separates amateur results from professional, vibrant, and brand-accurate products. It is the undisputed language of commercial printing, ensuring color consistency, cost-effectiveness, and the high-quality output that your brand deserves.
Ready to see your designs come to life with perfect color precision? Partner with Packaging Bird. Let our expertise in the CMYK process guarantee that your packaging and print materials always look their absolute best, right out of the box.
FAQs
1. What is the CMYK color model?
The CMYK color model is a subtractive colour system using cyan, magenta, yellow, and black inks to produce colours in printing.
2. What does CMYK stand for?
CMYK stands for Cyan, Magenta, Yellow, and Key (Black).
2. CMYK vs RGB: Which one should I use?
RGB is for digital displays, while CMYK is for print. Always convert to CMYK mode before sending designs to print.
3. Which color model is used in printed designs?
The CMYK model is used in commercial printing, as it aligns with how inks mix on paper.